Angular Navigation
This guide covers how routing works in an app built with Ionic and Angular.
The Angular Router is one of the most important libraries in an Angular application. Without it, apps would be single view/single context apps or would not be able to maintain their navigation state on browser reloads. With Angular Router, we can create rich apps that are linkable and have rich animations (when paired with Ionic of course). Let's look at the basics of the Angular Router and how we can configure it for Ionic apps.
A simple Route
For most apps, having some sort of route is often required. The most basic configuration looks a bit like this:
import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
@NgModule({
imports: [
...
RouterModule.forRoot([
{ path: '', component: LoginComponent },
{ path: 'detail', component: DetailComponent },
])
],
})
The simplest breakdown for what we have here is a path/component lookup. When our app loads, the router kicks things off by reading the URL the user is trying to load. In our sample, our route looks for '', which is essentially our index route. So for this, we load the LoginComponent. Fairly straight forward. This pattern of matching paths with a component continues for every entry we have in the router config. But what if we wanted to load a different path on our initial load?
Handling Redirects
For this we can use router redirects. Redirects work the same way that a typical route object does, but just includes a few different keys.
[
{ path: '', redirectTo: 'login', pathMatch: 'full' },
{ path: 'login', component: LoginComponent },
{ path: 'detail', component: DetailComponent },
];
In our redirect, we look for the index path of our app. Then if we load that, we redirect to the login route. The last key of pathMatch is required to tell the router how it should look up the path.
Since we use full, we're telling the router that we should compare the full path, even if ends up being something like /route1/route2/route3. Meaning that if we have:
{ path: '/route1/route2/route3', redirectTo: 'login', pathMatch: 'full' },
{ path: 'login', component: LoginComponent },
And load /route1/route2/route3 we'll redirect. But if we loaded /route1/route2/route4, we won't redirect, as the paths don't match fully.
Alternatively, if we used:
{ path: '/route1/route2', redirectTo: 'login', pathMatch: 'prefix' },
{ path: 'login', component: LoginComponent },
Then load both /route1/route2/route3 and /route1/route2/route4, we'll be redirected for both routes. This is because pathMatch: 'prefix' will match only part of the path.
Navigating to different routes
Talking about routes is good and all, but how does one actually navigate to said routes? For this, we can use the routerLink directive. Let's go back and take our simple router setup from earlier:
RouterModule.forRoot([
{ path: '', component: LoginComponent },
{ path: 'detail', component: DetailComponent },
]);
Now from the LoginComponent, we can use the following HTML to navigate to the detail route.
<ion-header>
<ion-toolbar>
<ion-title>Login</ion-title>
</ion-toolbar>
</ion-header>
<ion-content class="ion-padding">
<ion-button [routerLink]="['/detail']">Go to detail</ion-button>
</ion-content>
The important part here is the ion-button and routerLink directive. RouterLink works on a similar idea as typical hrefs, but instead of building out the URL as a string, it can be built as an array, which can provide more complicated paths.
We also can programmatically navigate in our app by using the router API.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
...
})
export class LoginComponent {
constructor(private router: Router){}
navigate(){
this.router.navigate(['/detail'])
}
}
Both options provide the same navigation mechanism, just fitting different use cases.
Navigating using LocationStrategy.historyGo
Angular Router has a LocationStrategy.historyGo method that allows developers to move forward or backward through the application history. Let's take a look at an example.
Say you have the following application history:
/pageA --> /pageB --> /pageC
If you were to call LocationStrategy.historyGo(-2) on /pageC, you would be brought back to /pageA. If you then called LocationStrategy.historyGo(2), you would be brought to /pageC.
An key characteristic of LocationStrategy.historyGo() is that it expects your application history to be linear. This means that LocationStrategy.historyGo() should not be used in applications that make use of non-linear routing. See Linear Routing versus Non-Linear Routing for more information.
Lazy loading routes
Now the current way our routes are setup makes it so they are included in the same chunk as the root app.module, which is not ideal. Instead, the router has a setup that allows the components to be isolated to their own chunks.
import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
@NgModule({
imports: [
...
RouterModule.forRoot([
{ path: '', redirectTo: 'login', pathMatch: 'full' },
{ path: 'login', loadChildren: () => import('./login/login.module').then(m => m.LoginModule) },
{ path: 'detail', loadChildren: () => import('./detail/detail.module').then(m => m.DetailModule) }
])
],
})
While similar, the loadChildren property is a way to reference a module by using native import instead of a component directly. In order to do this though, we need to create a module for each of the components.
...
import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { LoginComponent } from './login.component';
@NgModule({
imports: [
...
RouterModule.forChild([
{ path: '', component: LoginComponent },
])
],
})
We're excluding some additional content and only including the necessary parts.
Here, we have a typical Angular Module setup, along with a RouterModule import, but we're now using forChild and declaring the component in that setup. With this setup, when we run our build, we will produce separate chunks for both the app component, the login component, and the detail component.
Standalone Components
Standalone components is an experimental API introduced in Angular 14.x and available in Ionic 6.3 and later. This feature may change before it is stable.
Standalone components allow developers to lazy load a component on a route without having to declare the component to an Angular module.
To use standalone components with routing and Ionic Framework, you must first be on Ionic ^6.3.0. The experimental API requires developers to assign the EnvironmentInjector instance for each router outlet (ion-router-outlet and ion-tabs) that uses standalone component routing.
import { Component, EnvironmentInjector } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: 'app.component.html',
})
export class AppComponent {
constructor(public environmentInjector: EnvironmentInjector) {}
}
<ion-router-outlet [environmentInjector]="environmentInjector"></ion-router-outlet>
<!-- or if you are using ion-tabs -->
<ion-tabs [environmentInjector]="environmentInjector"> ... </ion-tabs>
Developers can use the existing syntax for standalone component routing from Angular:
@NgModule({
imports: [
RouterModule.forRoot([
{
path: 'standalone-route',
loadComponent: () => import('./path/to/my-component.component').then((c) => c.MyComponent),
},
]),
],
})
export class AppRoutingModule {}
To get started with standalone components visit Angular's official docs.
Live Example
If you would prefer to get hands on with the concepts and code described above, please checkout our live example of the topics above on StackBlitz.
Linear Routing versus Non-Linear Routing
Linear Routing
If you have built a web app that uses routing, you likely have used linear routing before. Linear routing means that you can move forward or backward through the application history by pushing and popping pages.
The following is an example of linear routing in a mobile app:
The application history in this example has the following path:
Accessibility --> VoiceOver --> Speech
When we press the back button, we follow that same routing path except in reverse. Linear routing is helpful in that it allows for simple and predictable routing behaviors. It also means we can use router Angular Router APIs such as LocationStrategy.historyGo().
The downside of linear routing is that it does not allow for complex user experiences such as tab views. This is where non-linear routing comes into play.
Non-Linear Routing
Non-linear routing is a concept that may be new to many web developers learning to build mobile apps with Ionic.
Non-linear routing means that the view that the user should go back to is not necessarily the previous view that was displayed on the screen.
The following is an example of non-linear routing:
In the example above, we start on the Originals tab. Tapping a card brings us to the Ted Lasso view within the Originals tab.
From here, we switch to the Search tab. Then, we tap the Originals tab again and are brought back to the Ted Lasso view. At this point, we have started using non-linear routing.
Why is this non-linear routing? The previous view we were on was the Search view. However, pressing the back button on the Ted Lasso view should bring us back to the root Originals view. This happens because each tab in a mobile app is treated as its own stack. The Working with Tabs sections goes over this in more detail.
If tapping the back button simply called LocationStrategy.historyGo(-1) from the Ted Lasso view, we would be brought back to the Search view which is not correct.
Non-linear routing allows for sophisticated user flows that linear routing cannot handle. However, certain linear routing APIs such as LocationStrategy.historyGo() cannot be used in this non-linear environment. This means that LocationStrategy.historyGo() should not be used when using tabs or nested outlets.
Which one should I choose?
We recommend keeping your application as simple as possible until you need to add non-linear routing. Non-linear routing is very powerful, but it also adds a considerable amount of complexity to mobile applications.
The two most common uses of non-linear routing is with tabs and nested ion-router-outlets. We recommend only using non-linear routing if your application meets the tabs or nested router outlet use cases.
For more on tabs, please see Working with Tabs.
For more on nested router outlets, please see Nested Routes.
Shared URLs versus Nested Routes
A common point of confusion when setting up routing is deciding between shared URLs or nested routes. This part of the guide will explain both and help you decide which one to use.
Shared URLs
Shared URLs is a route configuration where routes have pieces of the URL in common. The following is an example of a shared URL configuration:
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'dashboard',
component: DashboardMainPage,
},
{
path: 'dashboard/stats',
component: DashboardStatsPage,
},
];
The above routes are considered "shared" because they reuse the dashboard piece of the URL.
Nested Routes
Nested Routes is a route configuration where routes are listed as children of other routes. The following is an example of a nested route configuration:
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'dashboard',
component: DashboardRouterOutlet,
children: [
{
path: '',
component: DashboardMainPage,
},
{
path: 'stats',
component: DashboardStatsPage,
},
],
},
];
The above routes are nested because they are in the children array of the parent route. Notice that the parent route renders the DashboardRouterOutlet component. When you nest routes, you need to render another instance of ion-router-outlet.
Which one should I choose?
Shared URLs are great when you want to transition from page A to page B while preserving the relationship between the two pages in the URL. In our previous example, a button on the /dashboard page could transition to the /dashboard/stats page. The relationship between the two pages is preserved because of a) the page transition and b) the url.
Nested routes should be used when you want to render content in outlet A while also rendering sub-content inside of a nested outlet B. The most common use case you will run into is tabs. When you load up a tabs Ionic starter application, you will see ion-tab-bar and ion-tabs components rendered in the first ion-router-outlet. The ion-tabs component renders another ion-router-outlet which is responsible for rendering the contents of each tab.
There are very few use cases in which nested routes make sense in mobile applications. When in doubt, use the shared URL route configuration. We strongly caution against using nested routing in contexts other than tabs as it can quickly make navigating your app confusing.
Working with Tabs
With Tabs, the Angular Router provides Ionic the mechanism to know what components should be loaded, but the heavy lifting is actually done by the tabs component. Let's look at a simple example.
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'tabs',
component: TabsPage,
children: [
{
path: 'tab1',
children: [
{
path: '',
loadChildren: () => import('../tab1/tab1.module').then((m) => m.Tab1PageModule),
},
],
},
{
path: '',
redirectTo: '/tabs/tab1',
pathMatch: 'full',
},
],
},
{
path: '',
redirectTo: '/tabs/tab1',
pathMatch: 'full',
},
];
Here we have a "tabs" path that we load. In this example we call the path "tabs", but the name of the paths can be changed. They can be called whatever fits your app. In that route object, we can define a child route as well. In this example, the top level child route "tab1" acts as our "outlet", and can load additional child routes. For this example, we have a single sub-child-route, which just loads a new component. The markup for the tab is as follows:
<ion-tabs>
<ion-tab-bar slot="bottom">
<ion-tab-button tab="tab1">
<ion-icon name="flash"></ion-icon>
<ion-label>Tab One</ion-label>
</ion-tab-button>
</ion-tab-bar>
</ion-tabs>
If you've built apps with Ionic before, this should feel familiar. We create a ion-tabs component, and provide a ion-tab-bar. The ion-tab-bar provides a ion-tab-button with a tab property that is associated with the tab "outlet" in the router config. Note that the latest version of @ionic/angular no longer requires <ion-tab>, but instead allows developers to fully customize the tab bar, and the single source of truth lives within the router configuration.
How Tabs in Ionic Work
Each tab in Ionic is treated as an individual navigation stack. This means if you have three tabs in your application, each tab has its own navigation stack. Within each stack you can navigate forwards (push a view) and backwards (pop a view).
This behavior is important to note as it is different than most tab implementations that are found in other web based UI libraries. Other libraries typically manage tabs as one single history stack.
Since Ionic is focused on helping developers build mobile apps, the tabs in Ionic are designed to match native mobile tabs as closely as possible. As a result, there may be certain behaviors in Ionic's tabs that differ from tabs implementations you have seen in other UI libraries. Read on to learn more about some of these differences.
Child Routes within Tabs
When adding additional routes to tabs you should write them as sibling routes with the parent tab as the path prefix. The example below defines the /tabs/tab1/view route as a sibling of the /tabs/tab1 route. Since this new route has the tab1 prefix, it will be rendered inside of the Tabs component, and Tab 1 will still be selected in the ion-tab-bar.
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'tabs',
component: TabsPage,
children: [
{
path: 'tab1',
children: [
{
path: '',
loadChildren: () => import('../tab1/tab1.module').then((m) => m.Tab1PageModule),
},
],
},
{
path: 'tab1/view',
children: [
{
path: '',
loadChildren: () => import('../tab1/tab1view.module').then((m) => m.Tab1ViewPageModule),
},
],
},
{
path: 'tab2',
children: [
{
path: '',
loadChildren: () => import('../tab2/tab2.module').then((m) => m.Tab2PageModule),
},
],
},
{
path: 'tab3',
children: [
{
path: '',
loadChildren: () => import('../tab3/tab3.module').then((m) => m.Tab3PageModule),
},
],
},
],
},
{
path: '',
redirectTo: '/tabs/tab1',
pathMatch: 'full',
},
];
Switching Between Tabs
Since each tab is its own navigation stack, it is important to note that these navigation stacks should never interact. This means that there should never be a button in Tab 1 that routes a user to Tab 2. In other words, tabs should only be changed by the user tapping a tab button in the tab bar.
A good example of this in practice is the iOS App Store and Google Play Store mobile applications. These apps both provide tabbed interfaces, but neither one ever routes the user across tabs. For example, the "Games" tab in the iOS App Store app never directs users to the "Search" tab and vice versa.
Let's take a look at a couple common mistakes that are made with tabs.
A Settings Tab That Multiple Tabs Reference
A common practice is to create a Settings view as its own tab. This is great if developers need to present several nested settings menus. However, other tabs should never try to route to the Settings tab. As we mentioned above, the only way that the Settings tab should be activated is by a user tapping the appropriate tab button.
If you find that your tabs need to reference the Settings tab, we recommend making the Settings view a modal by using ion-modal. This is a practice found in the iOS App Store app. With this approach, any tab can present the modal without breaking the mobile tabs pattern of each tab being its own stack.
The example below shows how the iOS App Store app handles presenting an "Account" view from multiple tabs. By presenting the "Account" view in a modal, the app can work within the mobile tabs best practices to show the same view across multiple tabs.
Reusing Views Across Tabs
Another common practice is to present the same view in multiple tabs. Developers often try to do this by having the view contained in a single tab, with other tabs routing to that tab. As we mentioned above, this breaks the mobile tabs pattern and should be avoided.
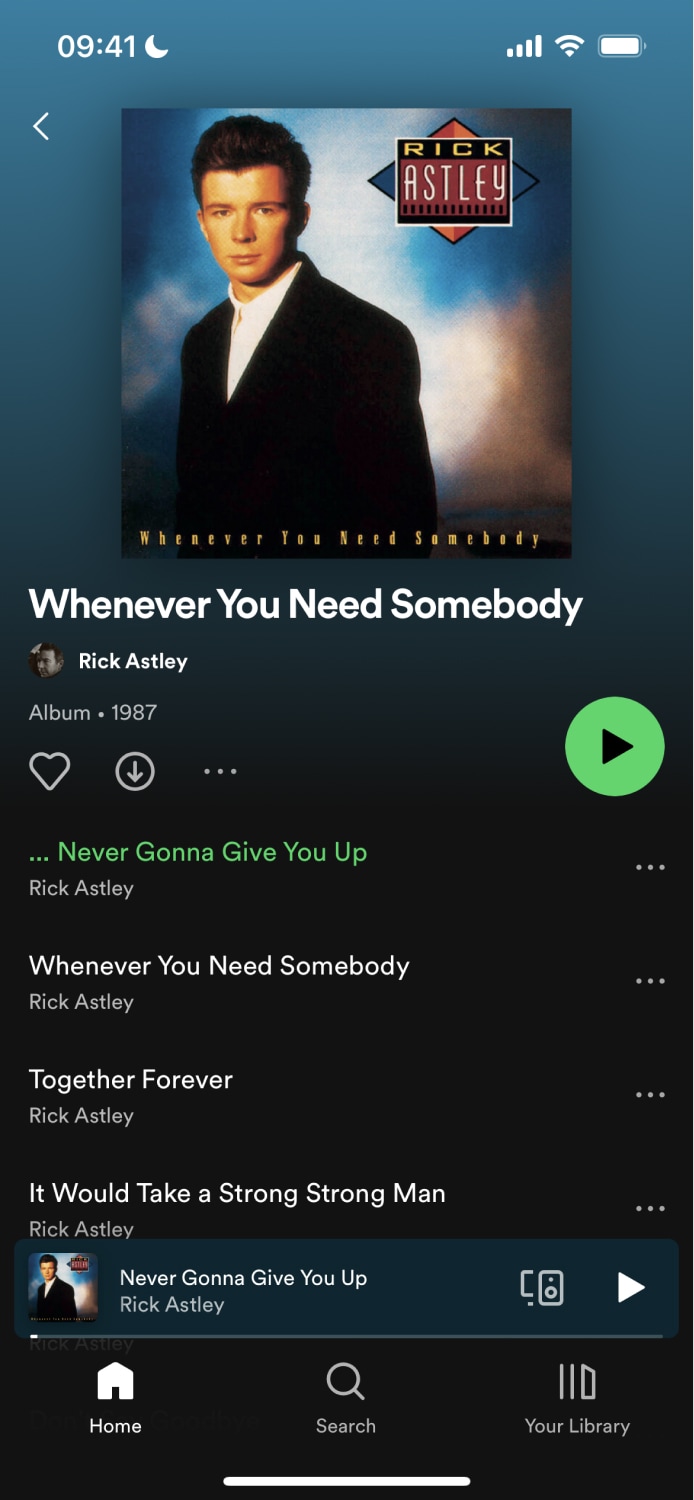
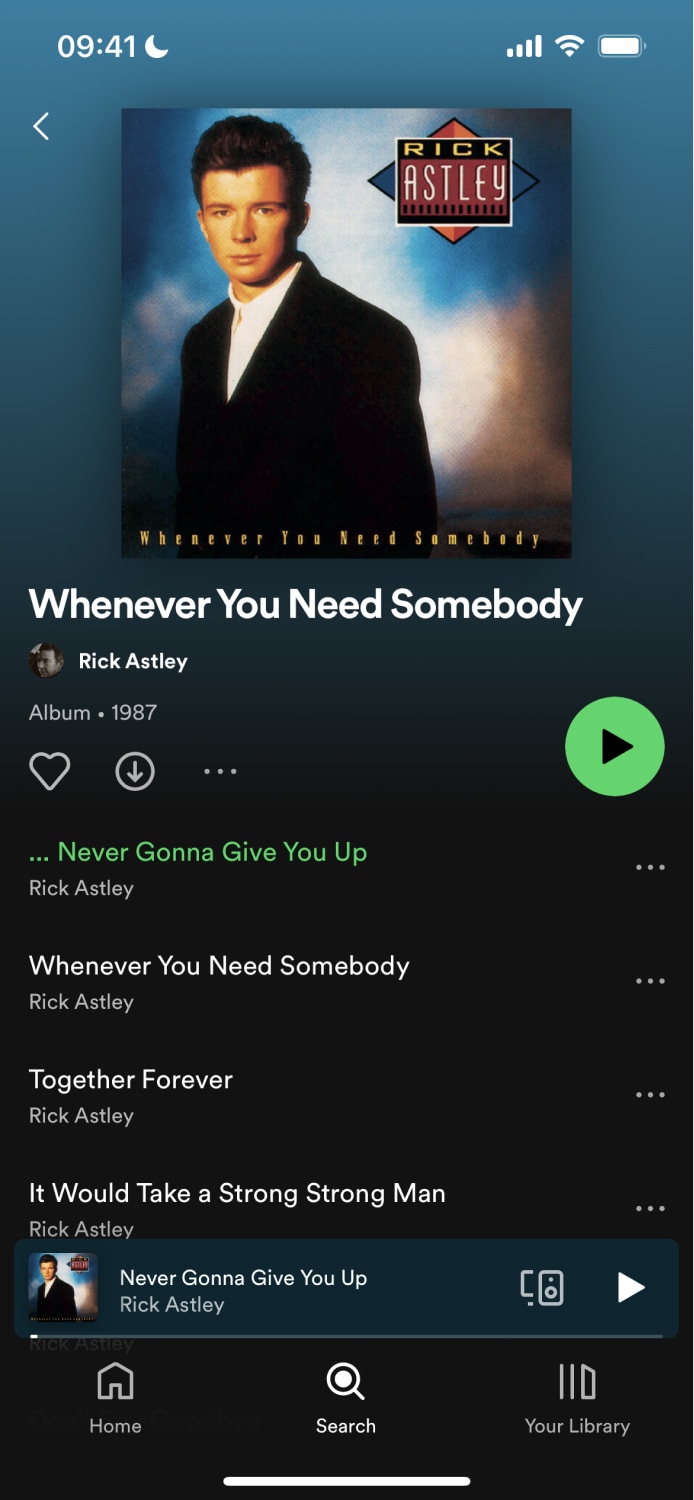
Instead, we recommend having routes in each tab that reference the same component. This is a practice done in popular apps like Spotify. For example, you can access an album or podcast from the "Home", "Search", and "Your Library" tabs. When accessing the album or podcast, users stay within that tab. The app does this by creating routes per tab and sharing a common component in the codebase.
The example below shows how the Spotify app reuses the same album component to show content in multiple tabs. Notice that each screenshot shows the same album but from a different tab.
| Home Tab | Search Tab |
|---|---|
 |  |